The genetic mutation behind Duchenne.
Understanding the cause of Duchenne begins with understanding the role of proteins and genes in how our bodies function.
Proteins are necessary for many important functions in the body, such as digesting our food, growing our bones, or—in the case of the protein called dystrophin—helping our muscles work properly.
Genes are made up of segments, called “exons,” that tell our cells which proteins to make. The dystrophin gene is made up of 79 exons that, when linked together, form the instructions for making dystrophin.

Meet Levi, age 10
Amenable to exon 45 skipping
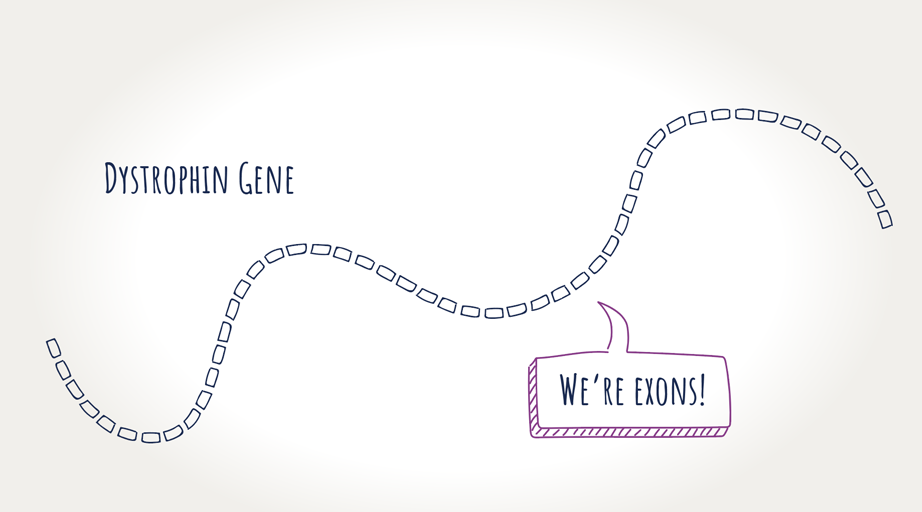
What is a genetic mutation?
A mutation is a change in a person's DNA. Mutations range in size from a small (a single rung on a ladder) to a large segment of DNA. Every mutation causes a different effect on our bodies. A mutation on the dystrophin gene means dystrophin is not produced—resulting in Duchenne.
3 common types of mutations.
Large deletions
One or more exons are missing
of people with Duchenne
Large duplications
One or more exons are duplicated
of people with Duchenne
Other changes
Small deletions or interruptions in the instructions
of people with Duchenne
About 9% of people diagnosed with Duchenne have a genetic mutation that is amenable to AMONDYS 45. Learn what this means.
AMONDYS 45 is used to treat patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) who have a confirmed mutation of the dystrophin gene that can be treated by skipping exon 45. The indication is approved under accelerated approval based on an increase in dystrophin production in skeletal muscle observed in patients treated with AMONDYS 45. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The importance of genetic testing.
While there is presently no cure for Duchenne, advances in research are ongoing. Genetic testing can now pinpoint the specific exons that are missing from the dystrophin gene. That’s why it’s so important for every child living with Duchenne to have a current genetic test—and for parents to understand the results.
If your child has a confirmed diagnosis of Duchenne, have they had a genetic test?
Yes,
a recent test, but I‘m not sure about the results.

Ask your child’s doctor to review the test to see if the genetic mutation is identified. Learn how to read the test results yourself.
Yes,
but it was several years ago.

Test methods have improved in recent years. Talk to your doctor about a retest to identify the mutation.

How is a genetic test performed? Getting a genetic test usually involves providing a blood or saliva sample.
1.
To confirm a Duchenne diagnosis
2.
To identify the genetic mutation and explore possible therapy options
3.
To facilitate potential clinical trial participation
4.
To assist with family planning
Related FAQs
A doctor will need to interpret the test results to consider appropriate treatment options. Learn more about deletions.
Weekly infusions of AMONDYS 45 helped the body make a shorter form of the dystrophin protein.a View the results from an ongoing clinical study.
AMONDYS 45 is used to treat patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) who have a confirmed mutation in the dystrophin gene that can be treated by skipping exon 45.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on an increase in dystrophin production in skeletal muscle observed in patients treated with AMONDYS 45. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification of a clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
aBoys treated with AMONDYS 45 showed varying levels of increased dystrophin production after 48 weeks. In an ongoing clinical study, 27 boys (median age 9 years) receiving AMONDYS 45 had an average dystrophin level of 1.74% of normal, compared to 0.76% in 16 boys who received a placebo infusion.